Have you ever wondered about the hidden secrets behind Liberica coffee? As you sip on your morning brew, there’s a world of unique magic waiting to be unraveled within each cup.
From the unusual botanical features of the Liberica coffee plant to the cultural and historical significance, there’s much to explore. Join us as we delve into the distinctive characteristics that set Liberica coffee apart, and uncover the fascinating elements that make it a standout in the world of coffee.
As a seasoned coffee connoisseur with years of experience in the industry, I have had the privilege of exploring the nuances of Liberica coffee and am excited to share my insights with you.
Discover All Liberica Coffee Characteristics

Now, let’s explore the rare gem of the coffee world, Liberica coffee, and its fascinating historical background and origin.
You’ll discover the unique characteristics that set Liberica apart from other coffee varieties, and gain a deeper understanding of its rich heritage.
Prepare to be amazed by the distinct flavors and aromas that make Liberica a standout in the world of coffee.
The Rare Gem of the Coffee World
Explore the unique characteristics of Liberica coffee, a rare gem in the world of coffee, known for its distinctive flavor and large beans.
Liberica coffee is a truly rare find, celebrated for its unique aroma and flavor profile. Its beans are significantly larger than those of other coffee varieties, and they exude a rich, fruity aroma that sets them apart.
The flavor of Liberica coffee is often described as bold and full-bodied, with complex notes that dance on your taste buds. It’s a coffee that stands out, offering a memorable and distinctive experience with every sip.
Embrace the rare and unique qualities of Liberica coffee, and indulge in the freedom of savoring a truly exceptional brew that defies the ordinary.
Historical Background and Origin
The unique characteristics of Liberica coffee, celebrated for its distinctive flavor and large beans, are deeply rooted in its historical background and origin.
Originating in Liberia, West Africa, Liberica coffee made its way to Southeast Asia during the colonial era. It quickly gained popularity for its resilience against pests and diseases, making it an attractive crop for cultivation.
The distinct flavor profile of Liberica coffee, often described as bold, full-bodied, and with a complex aroma, has contributed to its enduring appeal.
As a coffee enthusiast, you’ll appreciate the historical significance of Liberica coffee, as its journey from West Africa to Southeast Asia has shaped the unique traits that set it apart from other coffee varieties. Understanding its historical background and origin adds depth to the appreciation of Liberica coffee’s exceptional characteristics.
Unique Botanical Features of the Liberica Coffee Plant
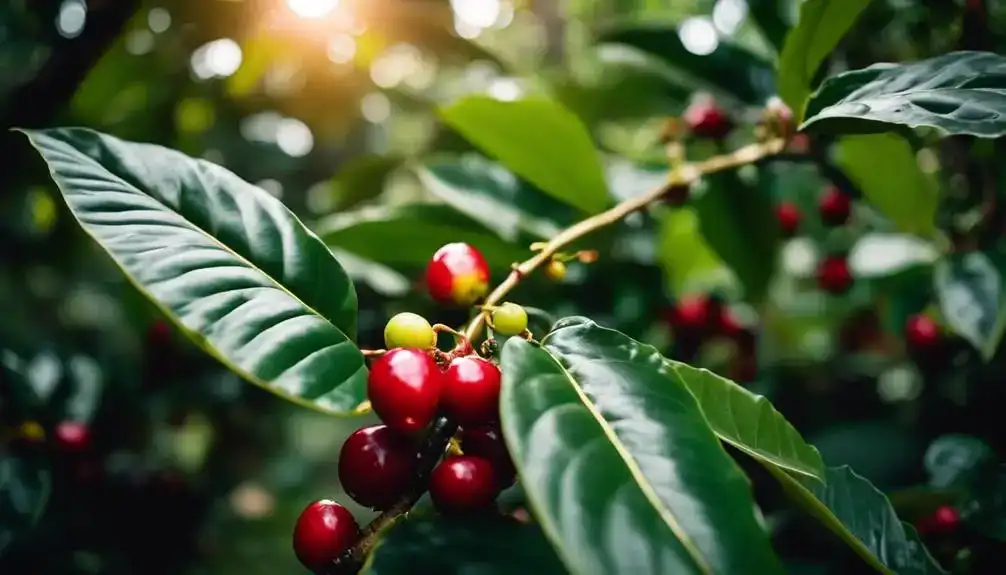

Hey, let’s talk about the unique botanical features of the Liberica coffee plant.
The leaf structure and size, flowering patterns and fragrance, and growth habit and size are all fascinating aspects of this majestic plant.
You’ll be amazed by the distinctive characteristics that set Liberica apart from other coffee varieties.
Leaf Structure and Size
With its large, broad leaves, the Liberica coffee plant possesses a unique botanical feature that sets it apart from other coffee varieties. The leaf size of the Liberica plant is notably larger compared to its counterparts, adding to its distinct appearance. The tree’s leaves can grow up to 8-12 inches in length and 4-6 inches in width, presenting a striking visual aspect in the coffee plantation.
This characteristic leaf size contributes to the overall grandeur of the Liberica plant, reflecting its robust and resilient nature. The plant’s leaf structure also plays a crucial role in its ability to capture sunlight efficiently, supporting its growth and bean morphology.
Liberica’s substantial leaf size and distinctive shape embody the freedom and individuality that this coffee plant represents.
- Large, broad leaves
- Leaf size: 8-12 inches in length, 4-6 inches in width
- Sunlight capture and support for growth
- Unique shape and appearance
- Reflects robust and resilient nature
Flowering Patterns and Fragrance
Liberica coffee’s remarkable botanical features extend beyond its large, broad leaves, as its flowering patterns and fragrance also contribute to its distinctiveness in the coffee world.
The liberica plant showcases a unique growth pattern, with delicate white flowers that bloom in clusters, creating a visually stunning display amidst its lush foliage. The fragrance of these blooms is captivating, offering a sweet and floral aroma that permeates the surrounding environment.
This distinctive aroma translates into the coffee beans, infusing them with enchanting floral notes that set liberica apart from other coffee varieties. When processing liberica coffee, the preservation of these floral characteristics is crucial to maintaining its unique essence.
Embracing the liberica aroma and flowering patterns adds a touch of freedom and individuality to your coffee experience, elevating it to a truly exceptional level.
Growth Habit and Size: The Majestic Presence of Liberica
When growing Liberica coffee, you’ll notice its majestic presence with its unique growth habit and size. The plant typically reaches impressive heights and spreads, making it stand out in comparison to other popular coffee varieties like Arabica and Robusta.
Visualizing the differences in size and growth habits will give you a better understanding of the distinct botanical features of the Liberica coffee plant.
Typical Height and Spread
Standing tall and commanding attention, the Liberica coffee plant typically reaches impressive heights and spreads out with an equally striking presence in its natural habitat. The plant’s typical height and spread are a testament to its unique magic and distinctiveness.
When cultivated, it showcases its majestic stature, making it an awe-inspiring sight. The significant height and spread of the Liberica coffee plant contribute to its distinctiveness in the world of coffee beans.
A Visual Comparison with Arabica and Robusta
Comparing the visual characteristics of Liberica, Arabica, and Robusta coffee plants reveals unique botanical features that showcase the majestic presence of Liberica in the world of coffee. Below is a visual comparison of the three coffee plants:Characteristic Liberica Arabica Robusta Plant Size Tall and robust Medium height Short and stout Leaf Size Large, elongated Large, oval Small, round Fruit Size Large, asymmetrical Small, round Small, round
Optimal Climate Conditions for Liberica Coffee
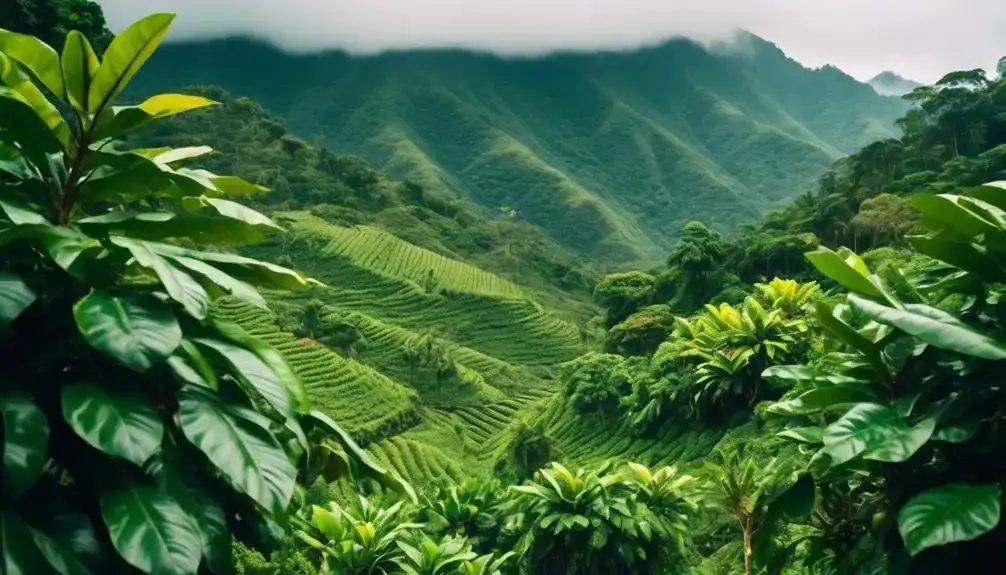

You need to understand the temperature ranges and rainfall patterns that are ideal for Liberica coffee cultivation.
Altitude and humidity also play a significant role in creating the optimal climate conditions for growing this unique coffee.
Temperature Ranges and Rainfall Patterns
Liberica coffee thrives in regions with consistent temperatures between 24 to 30 degrees Celsius and an annual rainfall of 1500 to 2500 millimeters. These optimal climate conditions play a crucial role in the growth and production of high-quality Liberica coffee. The table below illustrates the ideal temperature ranges and rainfall patterns for cultivating this unique coffee variety.
| Climate Factor | Optimal Range |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 24-30°C |
| Rainfall | 1500-2500mm |
| Altitude | 400-1000 meters |
The combination of these factors creates the perfect environment for Liberica coffee to flourish, ensuring that the soil and altitude complement the temperature and rainfall requirements. Understanding these essential climate conditions empowers you to cultivate and enjoy the distinct flavors of Liberica coffee.
The Impact of Altitude and Humidity on Liberica Cultivation
Altitude and humidity profoundly influence the cultivation of Liberica coffee, shaping its unique characteristics and flavor profile. When cultivating Liberica, consider the following:
- Altitude: Opt for elevations between 400 to 1,000 meters, allowing the beans to develop a rich, full-bodied flavor.
- Humidity: Seek regions with moderate humidity levels of 60-70%, promoting healthy plant growth and optimal bean development.
- Microclimate: Explore areas with diverse microclimates, as they can create distinct flavor profiles in Liberica beans.
- Terroir: Embrace the influence of terroir, as Liberica coffee exhibits exceptional adaptability to different soil and environmental conditions.
- Growing Conditions: Ensure well-drained soil and a balanced mix of sunshine and shade to support the growth of robust Liberica plants.
Understanding how altitude and humidity impact Liberica cultivation is essential for harnessing the full potential of this unique coffee variety.
Environmental Challenges and Adaptations

You’ll be interested in learning about Liberica coffee’s remarkable resilience to diseases and pests. These environmental challenges have led to innovative adaptations in the way Liberica coffee is grown and protected, making it a fascinating subject to explore.
Additionally, the sustainable farming practices that are crucial for the cultivation of Liberica coffee are worth examining. These practices ensure that the coffee is produced in an environmentally friendly manner, minimizing the negative impact on the ecosystem.
The ability of Liberica coffee to thrive in the face of these challenges is a testament to its adaptability and the ingenuity of those involved in its production. It is truly remarkable how farmers and researchers have found ways to overcome the obstacles posed by diseases and pests, making Liberica coffee a resilient and valuable crop.
Liberica’s Resilience to Diseases and Pests
With its robust nature and natural defenses, Liberica coffee demonstrates an impressive resilience to diseases and pests. Liberica’s resistance to common coffee diseases and pests makes it a desirable and low-maintenance option for coffee farmers. The table below highlights Liberica’s notable resistance to specific environmental challenges.Environmental Challenge Liberica’s Resistance Rust High Pests Strong Diseases Resilient Climate Change Adaptable
Liberica’s ability to withstand rust, pests, and diseases sets it apart from other coffee varieties, providing a reliable and sustainable option for coffee cultivation. Whether facing fluctuating climates or pest pressures, Liberica’s natural defenses make it an ideal choice for those seeking a coffee variety that thrives in the face of environmental challenges.
Sustainable Farming Practices for Liberica Cultivation
To ensure sustainable cultivation of Liberica coffee, farmers must adapt their farming practices to address environmental challenges and promote the coffee variety’s resilience. Embracing sustainable farming practices is crucial for the longevity of Liberica and the preservation of the coffee industry.
Here are some essential adaptations for sustainable Liberica cultivation:
- Agroforestry: Integrate shade trees to mimic natural forest ecosystems, providing habitat for wildlife and promoting soil health.
- Water Conservation: Implement drip irrigation systems and rainwater harvesting to efficiently manage water resources.
- Organic Fertilization: Utilize compost and organic matter to enrich the soil and minimize reliance on synthetic fertilizers.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Protect natural habitats and encourage diverse plant and animal species within the coffee farms.
- Soil Conservation: Employ cover crops and terracing techniques to prevent soil erosion and maintain soil structure.
Unraveling the Mystique: Size and Shape of Liberica Coffee Beans
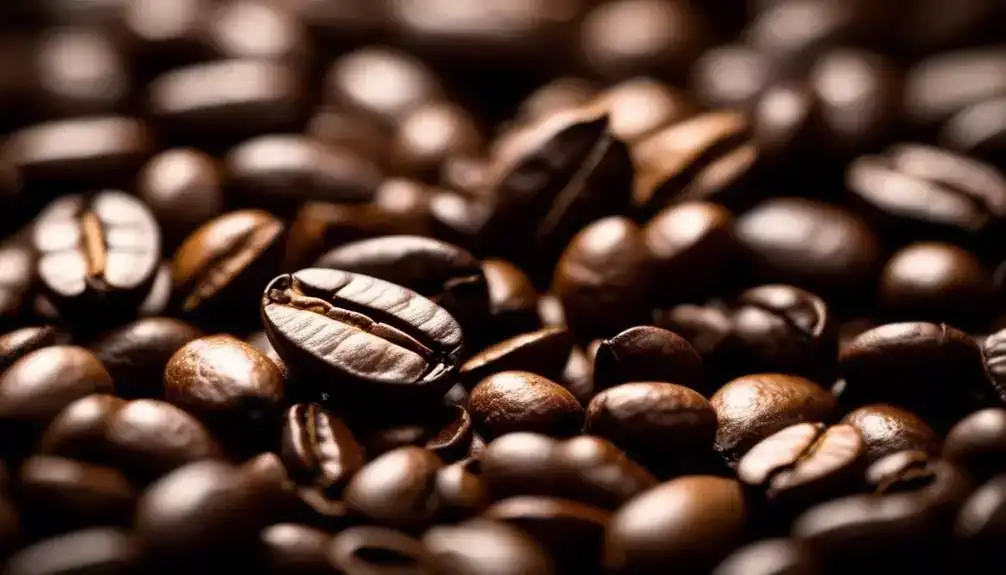

When you compare Liberica coffee beans to Arabica and Robusta beans, you can immediately notice their distinct size and shape. The visual differences are striking and offer a unique perspective on the diverse world of coffee beans.
Additionally, the various colors and textures of Liberica beans add to the mystique of this lesser-known coffee variety.
Visual Comparison with Arabica and Robusta Beans
Unveil the distinctive size and shape of Liberica coffee beans, comparing them visually with Arabica and Robusta beans. Liberica beans stand out with their large and asymmetrical shape, unlike the small and elongated Arabica beans or the round and compact Robusta beans. This visual comparison highlights the unique characteristics of Liberica beans within the coffee culture, offering a distinct appeal to those who value individuality and diversity in their coffee experience. Embracing the unconventional size and shape of Liberica beans adds a sense of freedom and adventure to the coffee ritual, allowing coffee enthusiasts to explore new dimensions of flavor and aroma. The table below provides a visual representation of the differences in bean size and shape among Liberica, Arabica, and Robusta beans.Bean Type Size Shape Liberica Large Asymmetrical Arabica Small Elongated Robusta Small Compact
The Palette of Colors and Textures of Liberica Beans
Unraveling the mystique of Liberica coffee beans, the palette of colors and textures adds another layer to the distinctive appeal of this unique coffee variety, building on its unconventional size and shape.
Liberica beans boast a captivating array of colors and textures, ranging from deep earthy browns to hints of mahogany and even an occasional maroon hue.
The textures are equally diverse, with some beans displaying a smooth and glossy surface, while others feature a more rugged and textured appearance.
This variety in color and texture reflects the rich diversity of Liberica coffee, adding to its allure and enigmatic charm.
The Complex Flavor Spectrum of Liberica Coffee

You’ll be amazed by the diverse range of flavor notes and aromatic qualities found in Liberica coffee.
Different processing methods play a significant role in shaping the unique flavor profile of this coffee variety.
The impact of these methods on flavor is truly fascinating and worth exploring.
Key Flavor Notes and Aromatic Qualities
When exploring the complex flavor spectrum of Liberica coffee, you’ll encounter a wide range of aromatic qualities and key flavor notes that contribute to its distinctive profile. Liberica coffee is known for its bold and complex flavors, offering a unique experience for those seeking something different. The bean size of Liberica is notably larger compared to other coffee species, which affects the brewing methods and the overall flavor profile. During cupping, you’ll notice the rich, full-bodied aroma with hints of floral and fruity notes, providing a truly liberating sensory experience. Embrace the freedom to experiment with different brewing methods to fully unlock the aromatic qualities and flavors of Liberica coffee, allowing you to savor its distinctive and captivating essence.
| Flavor Notes | Aromatic Qualities | Bean Size |
|---|---|---|
| Bold | Rich | Large |
| Floral | Full-bodied | |
| Fruity |
The Impact of Processing Methods on Flavor
Exploring the impact of processing methods on flavor in Liberica coffee reveals the intricate interplay between its bold, floral, and fruity notes, contributing to its complex flavor spectrum. The processing methods, such as fermentation and drying, greatly influence the taste, acidity, body, aftertaste, and overall complexity of Liberica coffee.
The quality of the bean size, roast, and grind also plays a vital role in enhancing the unique flavor notes of this speciality, single-origin coffee. Whether you prefer an organic brew or a specific roast, the processing methods are fundamental in bringing out the best in Liberica coffee.
Understanding the impact of processing methods on flavor empowers you to appreciate the full potential of Liberica coffee, allowing you to savor its distinct and captivating taste profile.
A Tale of Beans: Size, Shape, and Color Contrasts

When examining Liberica coffee beans, you’ll notice a stark contrast in size, shape, and color compared to other popular coffee varieties.
The larger size and unique kidney-like shape of Liberica beans set them apart from the smaller, rounder beans of Arabica and Robusta.
Additionally, the distinct color variations, from light brown to dark chocolate, contribute to the visual appeal of Liberica beans.
Cupping Notes: Liberica vs. Arabica vs. Robusta
In comparing Liberica, Arabica, and Robusta coffee beans, the differences in size, shape, and color are immediately apparent, revealing unique characteristics that contribute to each variety’s distinct flavor profile. When you engage in cupping, you’ll notice that Liberica beans are significantly larger and more irregular in shape compared to the more oval Arabica and round Robusta beans. Additionally, Liberica beans have a distinct light brown hue, while Arabica beans tend to be darker and Robusta beans appear almost black. The variations in size, shape, and color directly impact the flavors extracted during the bean processing stage, leading to the bold, fruity notes of Liberica, the aromatic, acidic flavors of Arabica, and the strong, nutty undertones of Robusta. Check out the table below for a quick visual comparison:Bean Type Size Shape Color Liberica Large Irregular Light brown Arabica Medium Oval Dark brown Robusta Small Round Almost black
Brewing Liberica Coffee: Techniques and Effects on Flavor Profile

When it comes to brewing Liberica coffee, the technique you choose can have a significant impact on the flavor profile. Whether you opt for drip, French press, or espresso methods, each approach can bring out different nuances in the coffee’s taste.
Understanding the art of brewing Liberica coffee is essential for unlocking its full potential and delivering a satisfying cup of java.
Comparing Drip, French Press, and Espresso Methods
To achieve the best flavor profile when brewing Liberica coffee, it’s essential to understand the differences in techniques and effects between drip, French press, and espresso methods. Each method offers a unique way to extract the rich and unique magic of Liberica coffee, resulting in distinct flavor profiles and aromas.
- *Drip Method*: This classic technique allows for a clean and bright cup, highlighting the fruity and floral notes of Liberica coffee.
- *French Press*: With this method, you can experience the full-bodied and robust characteristics of Liberica, enhancing its earthy and nutty undertones.
- *Espresso*: The intense pressure and rapid extraction of espresso bring out the bold and complex flavors of Liberica, producing a rich and creamy beverage.
- *Temperature and Time*: Adjusting the brewing temperature and time can significantly impact the flavor profile of Liberica coffee.
- *Grind Size*: The coarseness or fineness of the coffee grounds plays a crucial role in extracting the desired flavors from Liberica beans.
Understanding these methods empowers you to tailor your brewing approach to fully appreciate the unique characteristics of Liberica coffee.
The Art of Brewing Perfect Liberica Coffee
Maximize the rich and unique characteristics of Liberica coffee by mastering the art of brewing it to perfection. When selecting brewing methods for Liberica coffee, consider its distinct flavors. The unique bean processing of Liberica coffee requires a balance between the brewing technique and the bean’s natural acidity.
French press brewing can enhance the full-bodied and nutty flavors, while drip brewing can highlight its fruity and floral notes. Understanding the bean processing and experimenting with different brewing methods will allow you to unlock the diverse flavors of Liberica coffee.
Achieving the perfect brew is about finding the right balance between bean processing and brewing technique. Embrace the freedom to explore various methods until you discover the perfect way to brew Liberica coffee that suits your individual taste preferences.
Health Benefits and Caffeine Content

You’ll be interested to learn about the health benefits of Liberica coffee and how its caffeine content compares to other popular coffee varieties.
Liberica coffee offers unique health advantages that you may not be aware of, and understanding its caffeine content in comparison to Arabica and Robusta can help you make informed choices about your coffee consumption.
Exploring the Health Benefits of Liberica Coffee
Liberica coffee offers potential health benefits and a moderate caffeine content, making it an intriguing choice for coffee enthusiasts seeking a unique flavor profile.
When it comes to health benefits, Liberica coffee is rich in antioxidants, which can help in fighting inflammation and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Additionally, its distinct flavors and aroma are a result of the unique processing methods and farming techniques employed during its harvest. The beans are often processed using the dry method, enhancing the coffee’s robust flavor profile.
Liberica coffee is also known for its smooth, full-bodied texture, making it a delightful choice for those who savor the freedom to explore new and unconventional coffee experiences.
Caffeine Content: Liberica vs. Arabica vs. Robusta
As you compare Liberica, Arabica, and Robusta coffee, consider their caffeine content and health benefits, building on the unique attributes of Liberica coffee previously discussed. Liberica coffee generally has a lower caffeine content compared to Robusta but slightly higher than Arabica. However, caffeine content can vary based on factors like bean processing and brewing methods. Here’s a comparison of the approximate caffeine content per 8 oz cup for each type of coffee:Coffee Type Caffeine Content (per 8 oz cup) Liberica 95-200 mg Arabica 70-120 mg Robusta 150-175 mg
Understanding these differences allows you to make an informed choice based on your caffeine preferences and health considerations. Whether you prefer the boldness of Robusta, the nuanced flavors of Arabica, or the unique profile of Liberica, there’s a coffee for every freedom-loving individual’s taste.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations

When considering Liberica coffee, it’s important to address the environmental and sustainability aspects of its cultivation.
Liberica coffee plays a significant role in sustainable agriculture, and it’s crucial to understand the environmental challenges associated with its production.
The Role of Liberica Coffee in Sustainable Agriculture
Playing a crucial role in sustainable agriculture, Liberica coffee offers unique environmental and sustainability considerations that set it apart from other coffee varieties.
When it comes to liberica farming, its cultivation promotes biodiversity and reduces the environmental impact. Liberica production involves minimal pesticide use, contributing to healthier ecosystems.
The shade-grown nature of liberica coffee encourages forest preservation and provides habitat for birds and other wildlife. Additionally, its cultivation at higher elevations minimizes water usage and soil erosion, further contributing to sustainable agriculture.
This approach not only ensures the preservation of the natural environment but also supports the livelihoods of local communities. Embracing liberica coffee aligns with sustainable agricultural practices, making it an environmentally conscious choice for coffee enthusiasts.
Addressing Environmental Challenges in Liberica Coffee Cultivation
Addressing environmental challenges in liberica coffee cultivation requires a comprehensive understanding of its unique characteristics and the implementation of sustainable farming practices. Liberica coffee, with its distinct taste and flavors, presents specific environmental challenges that need to be addressed for sustainable cultivation.
When considering the environmental impact of liberica coffee bean processing, it’s essential to prioritize methods that minimize water usage and reduce waste. Additionally, promoting biodiversity within coffee plantation ecosystems can help mitigate environmental challenges and support the long-term health of the coffee bean crops.
Implementing efficient waste management systems and utilizing organic farming practices can further contribute to environmental sustainability in liberica coffee cultivation. By embracing these strategies, you can actively participate in preserving the natural environment while enjoying the unique qualities of liberica coffee.
Cultural and Historical Significance of Liberica Coffee

Let’s explore the cultural and historical significance of Liberica coffee.
This unique coffee variety has deep roots in local traditions and practices, playing a significant role in the cultural fabric of many regions.
Additionally, tracing the global journey of Liberica coffee from its origin to the cup provides valuable insights into its historical importance and widespread impact.
Liberica Coffee in Local Traditions and Practices
Liberica coffee holds a significant place in local traditions and practices, contributing to the cultural and historical tapestry of the regions where it’s cultivated. The unique characteristics of Liberica, from its distinct bean shape to its preference for specific growing regions and soil composition, have woven it into the fabric of various cultures.
In many places, the history of Liberica coffee is intertwined with local customs and rituals, becoming a symbol of hospitality and community. Some ways in which Liberica coffee is integrated into local traditions include:
- Being used in traditional coffee ceremonies
- Playing a central role in social gatherings and celebrations
- Serving as a symbol of cultural identity
- Being offered as a gesture of friendship and respect
- Featuring in local legends and stories
The rich history and cultural significance of Liberica coffee reflect its deep-rooted importance in the communities where it’s cherished.
The Global Journey of Liberica Coffee: From Origin to Cup
How has the cultural and historical significance of Liberica coffee shaped its global journey from origin to cup?
Liberica coffee’s unique magic lies not only in its bold, fruity flavor but also in its rich cultural and historical significance. From its origins in West Africa, where it was first discovered, to its introduction to Southeast Asia and the Philippines during the colonial era, Liberica coffee has traversed continents, carrying with it a tapestry of traditions and stories.
Its journey reflects the intertwining of diverse cultures and the resilience of a coffee variety often overshadowed by its counterparts. As Liberica coffee makes its way from the farms where it’s grown to the cups of coffee lovers worldwide, it continues to symbolize the untold narratives and the unyielding spirit of freedom and diversity.
Conclusion
You’ve just scratched the surface of the unique magic of Liberica coffee.
Did you know that the average size of a Liberica coffee bean is almost double that of the more common Arabica bean? Imagine the impact that has on the flavor and aroma of your morning cup.
With its rich history, distinct flavor profile, and environmental adaptability, Liberica coffee is truly a fascinating and valuable addition to the world of coffee.